Radiant Floor Heating Design Considerations in Luxury Homes
When it comes to creating a comfortable and energy-efficient home environment, heated floors are a popular choice for high-end residential properties. Radiant floor heating, in particular, offers a modern solution that not only enhances comfort but also integrates seamlessly with luxury residential designs. In this article, we will explore the concept of radiant floor heating,…
Morgan Poulos Keating, PE
July 8, 2024
12 mins read

When it comes to creating a comfortable and energy-efficient home environment, heated floors are a popular choice for high-end residential properties. Radiant floor heating, in particular, offers a modern solution that not only enhances comfort but also integrates seamlessly with luxury residential designs. In this article, we will explore the concept of radiant floor heating, the various types, the benefits it offers, and important design considerations.
What is Radiant Floor Heating?
Radiant floor heating is an advanced heating method designed to provide consistent and comfortable warmth by installing heating elements beneath the floor surface. This innovative approach is particularly favored in residential spaces for its efficiency, aesthetic benefits, and ability to enhance overall comfort.
Basics of Underfloor Heating Systems
Underfloor heating, also known as radiant floor heating, functions by warming the floor itself, which then radiates heat upward into the living space. This system eliminates the need for traditional heating methods such as radiators or forced-air systems, creating a more efficient and aesthetically pleasing solution.
The heating elements used in underfloor heating can be either electric cables or mats, or hydronic tubing that circulates warm water. These elements are strategically installed beneath the flooring material, ensuring that heat is evenly distributed across the entire surface.
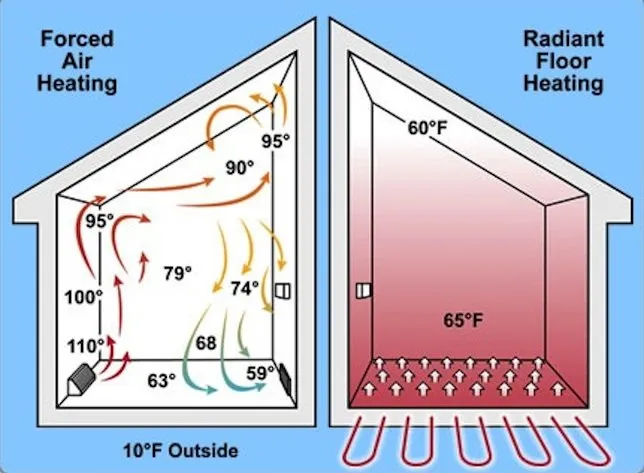
How Underfloor Heating Works
The operation of a radiant floor system involves a simple yet effective process:
- Heat generation: The heating elements, whether electric or hydronic, generate heat when the system is activated. This heat is transferred to the floor material above the elements.
- Heat radiation: Once the floor material is heated, it radiates warmth evenly throughout the room, creating a comfortable and consistent indoor temperature.
- Temperature control: Modern underfloor heating systems are equipped with thermostats and zoning controls, allowing homeowners to set and maintain their desired temperature with precision. This ensures optimal comfort and energy efficiency by heating only the areas in use.
Underfloor heating offers a discreet heating solution that seamlessly integrates with interior layout and design of a space, enhancing both comfort and energy efficiency.
Types of Radiant Floor Heating
Radiant floor heating systems are designed to provide efficient and uniform warmth by heating the floor surface directly. There are two primary types of radiant floor heating systems: hydronic systems and electric systems. Each type has its unique features, advantages, and applications, making them suitable for different residential heating needs.
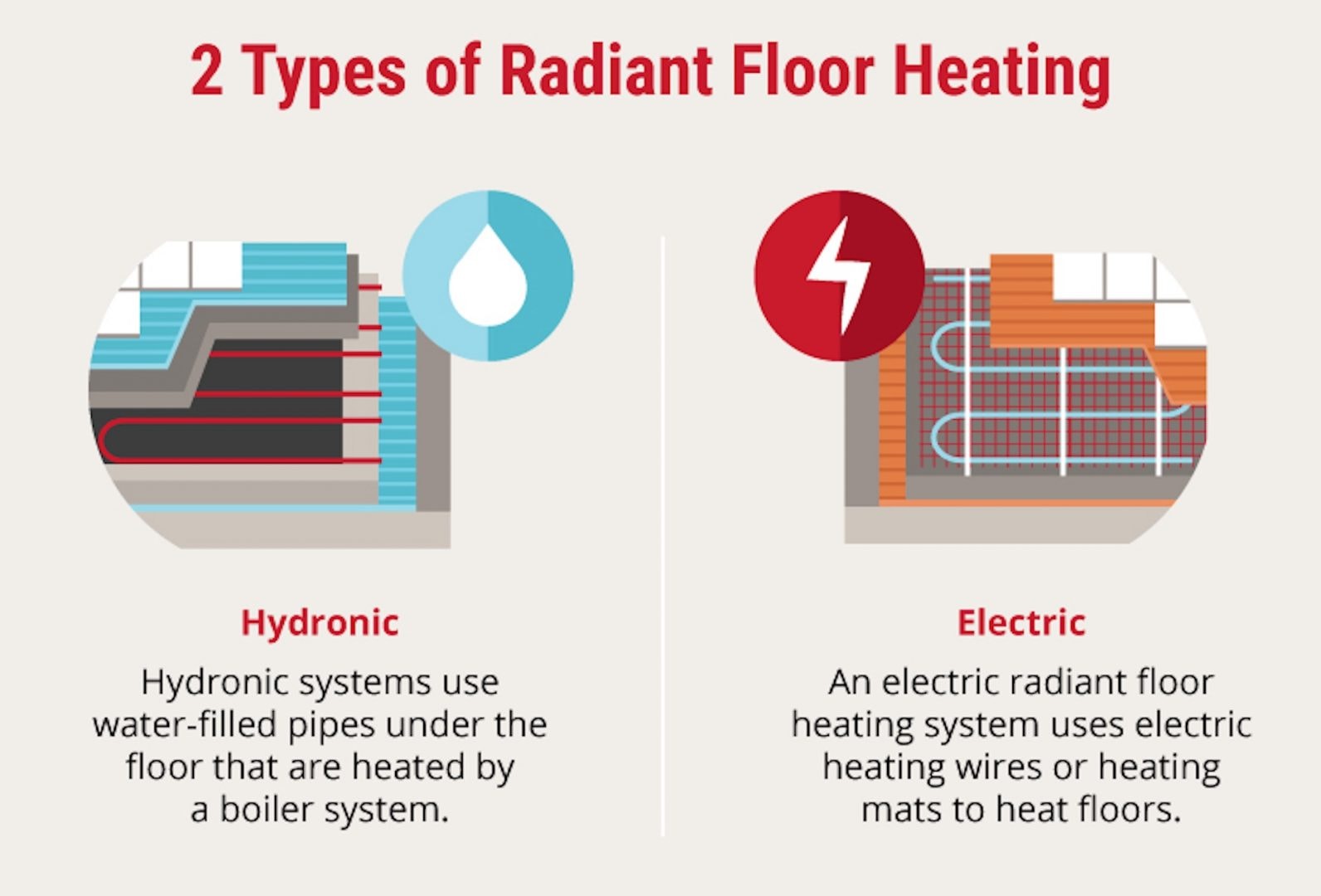
Hydronic Radiant Floor Heating Systems
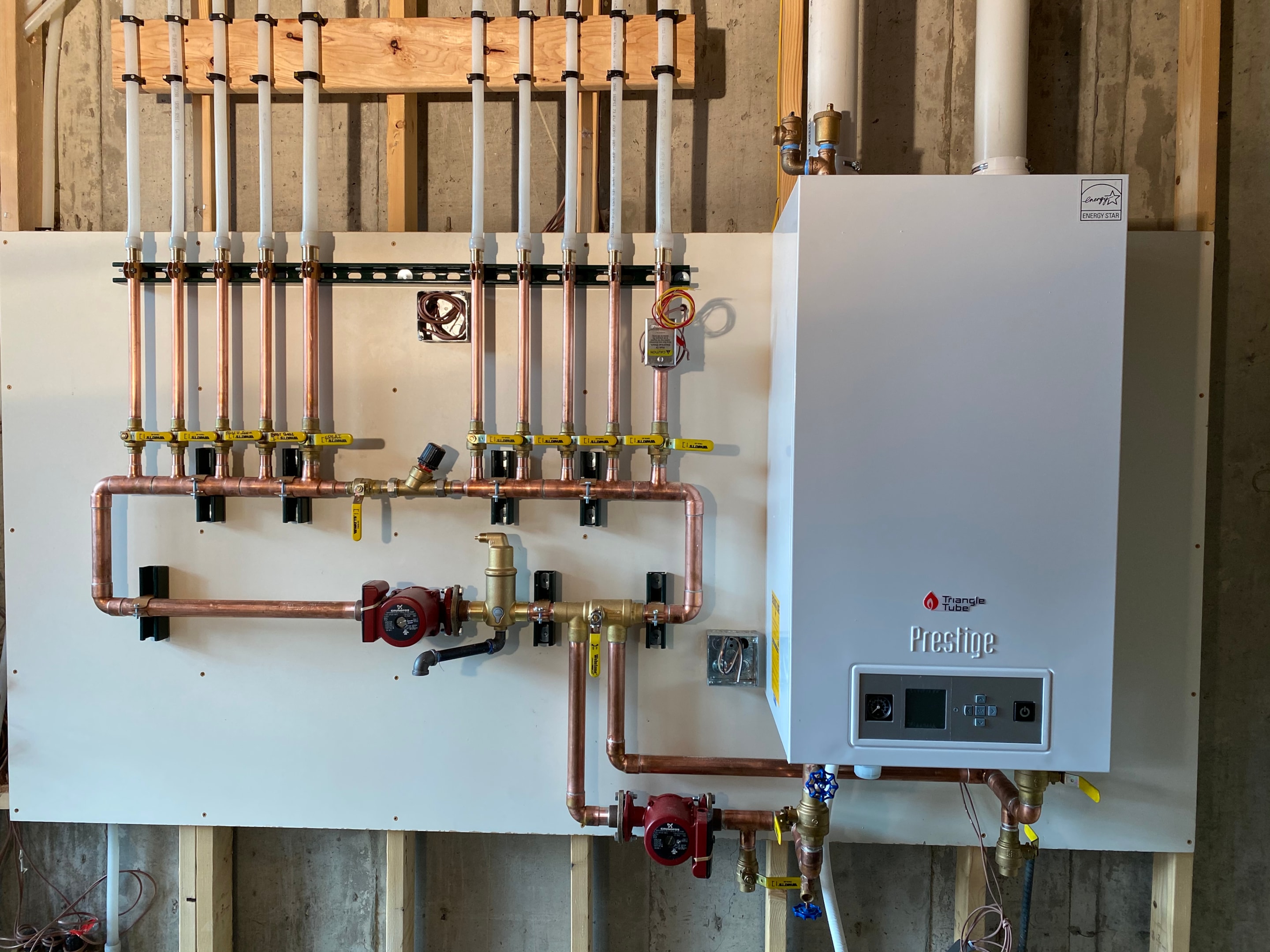
Hydronic radiant floor heating systems are highly efficient and are often the preferred choice for larger installations and new constructions. These systems use water heated by a boiler or water heater, which is circulated through a network of pipes embedded in the floor.
Here’s an in-depth look at hydronic systems.
Components: The main components of a hydronic system include a boiler or water heater, a manifold for distributing water, and a network of PEX (cross-linked polyethylene) tubing laid out in a pattern beneath the floor. The system also includes pumps, valves, and thermostats to regulate water flow and temperature.
Installation: Hydronic systems are typically installed in a concrete slab or over a subfloor. The PEX tubing is embedded in the concrete or installed within specially designed panels that ensure even heat distribution. This type of installation is most feasible during the construction phase of a new home or during major renovations.
Operation: Water is heated to a set temperature by the boiler and circulated through the PEX tubing. The heated water transfers its warmth to the floor, which then radiates heat upwards into the living space. Hydronic systems can be zoned to provide different temperatures in different areas of the home, enhancing user comfort and energy efficiency.
Advantages: Hydronic systems are highly efficient, especially in larger spaces, due to the high thermal mass of water, which retains and distributes heat effectively. They offer lower operating costs over time, especially when paired with high-efficiency boilers or alternative heat sources like solar water heaters. Additionally, these systems provide a consistent and comfortable heat without the noise or drafts associated with forced-air systems.

Electric Radiant Floor Heating Systems
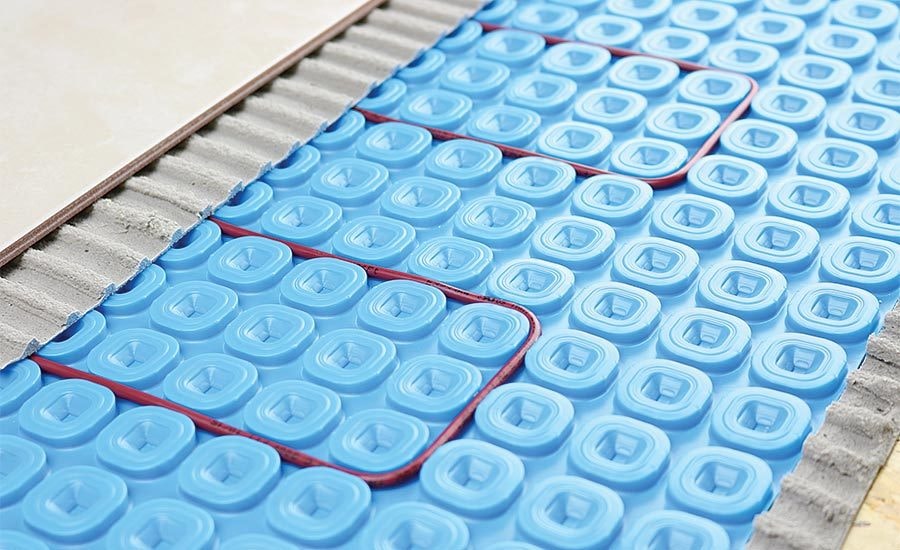
Electric radiant floor heating systems are an excellent option for smaller spaces, retrofits, and specific applications where hydronic systems may not be practical or feasible. These systems use electric heating cables or mats installed beneath the flooring material to generate heat.
Here’s a detailed overview of the electric radiant heating system.
Components: Electric systems consist of heating cables or mats, a thermostat for temperature control, and electrical connections. The heating elements can be installed directly under various types of flooring, including tile, stone, laminate, and engineered wood.
Installation: Electric radiant heating systems are relatively easy to install, making them ideal for remodeling projects and retrofits. However, hiring a professional to install radiant floor heating is recommended to ensure proper setup and safety. The heating cables can be laid out in a custom pattern to fit the specific area, or pre-configured mats can be used for quicker installation. They are typically embedded in a thin layer of mortar or self-leveling compound to ensure even heat distribution.
Operation: When the system is activated, electricity flows through the heating cables or mats, generating heat. This heat is transferred to the floor surface and radiates upwards into the room. Electric systems are controlled by programmable thermostats, allowing homeowners to set schedules and maintain precise temperatures.
Advantages: Electric systems are straightforward to install and can be up and running quickly, making them ideal for smaller spaces such as bathrooms, kitchens, or individual rooms. They provide rapid heat-up times and precise temperature control, enhancing comfort and convenience. Furthermore, they often require minimal maintenance compared to hydronic systems.
Both hydronic and electric radiant floor heating systems offer unique benefits and are suited for different applications. Hydronic systems excel in larger spaces and new constructions with greater efficiency and lower long-term costs, while electric systems provide flexibility, ease of installation, and precise control, making them ideal for smaller or retrofit projects or even specific spaces in a home. Understanding the individual needs of the finalized space can help facilitate the selection of the optimal radiant floor heating system for enhanced performance and comfort.

Benefits of Radiant Heating Systems
Underfloor heating systems offer a range of advantages that make them an attractive option for high-end residential spaces.
Energy Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
Underfloor heating systems are renowned for their energy efficiency. By distributing heat evenly across the floor surface, these systems can maintain a comfortable indoor temperature at lower thermostat settings compared to traditional heating methods. This results in significant energy savings. Hydronic systems, in particular, are highly efficient because they use water as a heat transfer medium, which retains and distributes heat more effectively than air. Over time, the reduced energy consumption translates into lower utility bills, making underfloor heating a cost-effective solution for homeowners.
Increased Comfort & Quiet
One of the standout benefits of underfloor heating systems is the enhanced comfort they provide. The heat radiates uniformly from the floor, eliminating cold spots and creating a consistent temperature throughout the room. This gentle, radiant heat is particularly pleasant compared to the intermittent blasts of hot air from traditional forced-air systems. Underfloor heating systems also operate silently, avoiding the noise pollution associated with radiators, vents, and fans, contributing to a peaceful and quiet living space.
Improved Indoor Air Quality
Underfloor heating systems contribute to better indoor air quality by reducing the circulation of dust, allergens, and other airborne particles. Unlike forced-air systems, which can blow dust and allergens around the house, radiant heating systems provide warmth without moving air. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with allergies or respiratory conditions, as it creates a cleaner and healthier indoor environment.
Smart Thermostat Compatibility
Modern underfloor heating systems are compatible with smart thermostats, offering precise control over temperature settings and energy usage. Smart thermostats allow homeowners to program heating schedules, monitor energy consumption, and adjust temperatures remotely via smartphone apps. This level of control not only enhances convenience but also further optimizes energy efficiency by ensuring the heating system operates only when needed. The ability to integrate with home automation systems adds another layer of sophistication and convenience to high-end residential homes.
Low Maintenance
Underfloor heating systems require minimal maintenance compared to traditional heating systems. Electric systems have no moving parts and are generally maintenance-free once installed. Hydronic systems, while slightly more complex, also have low maintenance needs. The primary components, such as the boiler and pumps, require periodic checks, but the tubing and manifold system are designed for long-term reliability. This ensures that homeowners can enjoy the benefits of underfloor heating without the hassle of frequent upkeep or repairs.
From energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness to increased comfort, improved indoor air quality, smart thermostat compatibility, and low maintenance, radiant heating systems enhance the overall living experience while providing practical advantages. For homeowners seeking a sophisticated, efficient, and comfortable heating solution, underfloor heating is an excellent choice.
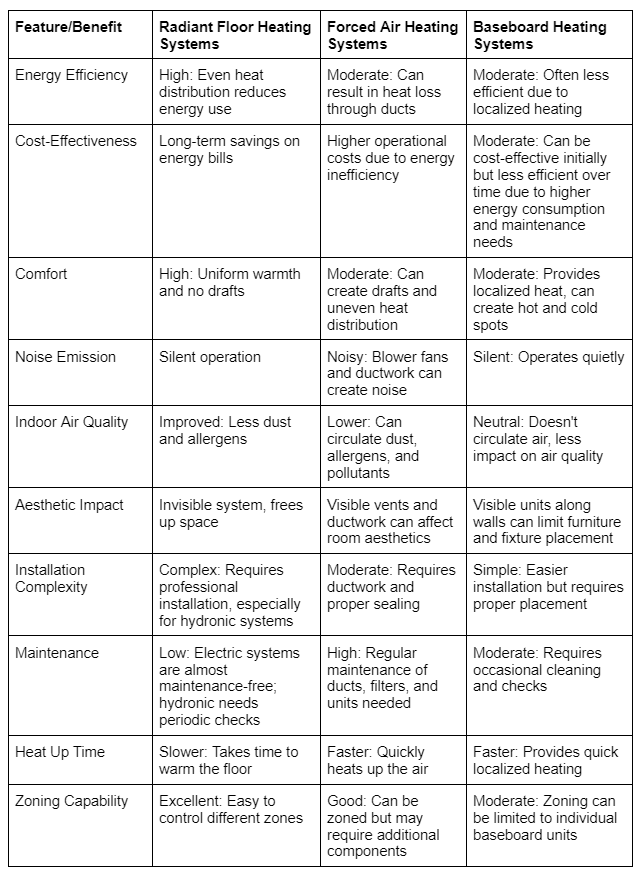
Comparing Radiant Floor Heating to Other Conventional Heating Systems
To provide a comprehensive understanding of the advantages and disadvantages of different heating systems, the following table compares radiant floor heating systems with conventional alternatives like forced air and baseboard heating:
Radiant Floor Heating Design Considerations
Designing an effective radiant floor heating system involves several important considerations to ensure optimal performance, efficiency, and comfort.
Compatible Flooring Materials
Choosing the right flooring material impacts the efficiency and effectiveness of a radiant floor heating system. Here are some compatible flooring options:
- Tile and stone: These materials have high thermal conductivity, making them ideal for radiant floor heating systems. They quickly and efficiently transfer heat from the heating elements to the room.
- Laminate and vinyl: These materials can also work well with radiant floor heating, provided they are compatible with the system specifications. It’s important to select high-quality products designed for use with underfloor heating.
- Wood flooring: While wood flooring can be used with radiant floor heating systems, there are specific considerations to keep in mind:
- Engineered wood: This type of wood is more stable than solid wood and is less likely to warp or shrink with temperature changes, making it the preferred choice for radiant heating.
- Moisture content: It is essential to ensure that the wood has low moisture content to prevent expansion and contraction, which can lead to warping and damage to the flooring.
- Temperature control: Maintaining a consistent temperature is crucial to avoid overheating, which can damage the wood.
Insulation Recommendations
Proper insulation is essential to maximize the efficiency of a radiant floor heating system. Insulation prevents heat loss to the subfloor and ensures that the heat is directed upwards into the living space. Recommendations include:
- Insulation boards: Rigid insulation boards installed beneath the heating elements help to reflect heat upwards.
- Edge insulation: Installing insulation around the perimeter of the heated floor area prevents heat loss to adjacent rooms and structural elements.
- Subfloor preparation: Ensuring that the subfloor is well-insulated and free of drafts can significantly enhance the system’s efficiency.
System Sizing, Zoning, and Selection
Correct sizing and zoning of the radiant floor heating system are crucial for efficient operation and comfort. Key considerations include:
- Heat load calculation: Calculate the heat load for each zone to ensure the system is sized correctly. This involves considering factors such as room size, insulation levels, and desired indoor temperature.
- Zoning: Divide the home into different heating zones to allow for individual temperature control. This increases comfort and can result in energy savings.
- Boiler selection: For hydronic systems, selecting the right boiler is critical. Some factors to consider include:
- Boiler capacity: Ensure the boiler has sufficient capacity to meet the heating demands of all zones.
- Efficiency: Choose high-efficiency boilers to maximize energy savings.
- Compatibility: Ensure the boiler is compatible with the radiant floor heating system components and control systems.

Cost
Radiant floor heating cost can vary based on several factors:
System type: Hydronic systems generally have higher initial costs due to the complexity of installation and equipment. However, they offer lower operating costs over time.
Installation complexity: New constructions may have lower installation costs compared to retrofitting an existing home.
Flooring material: The choice of flooring material can impact costs, with materials like tile and stone often being more expensive than laminate or vinyl.
Energy savings: While the initial investment may be higher, the long-term energy savings and increased home value can offset the installation costs.
By considering these design factors when installing radiant floor heating, homeowners can ensure that their radiant floor heating system is efficient, effective, and tailored to their specific needs.
Our Expertise at DAE
DAE brings extensive expertise in designing and implementing different heating systems, including radiant floor heating, for high-end residential homes. Our team excels in crafting tailored solutions that integrate seamlessly with the architectural and aesthetic visions of finished spaces. DAE’s approach focuses on precision engineering, ensuring that each system is optimized for efficiency and performance without compromising the overall design goals of the project. Our team provides comprehensive support from the initial design phase through to installation, ensuring that the selected heating system meets the highest standards of quality and reliability.
Looking to integrate radiant floor heating into your home? Let DAE help you assess your options and make the best decision for your specific needs. Contact us today to discuss your project and learn more about our tailored solutions.