What is a HERS Score? Decoding the Home Energy Rating Index
Energy efficiency has become a critical consideration for architects, engineers, homeowners and builders. The quest for a greener, more cost-effective living environment is driving the need for a comprehensive understanding of home energy performance. The HERS Index (a score determined through a HERS rating) developed by RESNET, is a nationally recognized system for inspecting and…
Morgan Poulos Keating, PE
June 4, 2024
12 mins read

Energy efficiency has become a critical consideration for architects, engineers, homeowners and builders. The quest for a greener, more cost-effective living environment is driving the need for a comprehensive understanding of home energy performance. The HERS Index (a score determined through a HERS rating) developed by RESNET, is a nationally recognized system for inspecting and calculating a home’s energy performance.
In this article, we explore the various aspects that contribute to assessing a home’s energy performance. From the factors that influence energy ratings to the methodology behind these assessments, we delve into the key components that make up the Home Energy Rating Index.
Understanding the HERS Index
As the drive for energy efficiency intensifies, tools like the HERS Index have become indispensable in both residential and commercial construction. This nationally recognized scoring system is the industry standard for benchmarking energy performance and guiding improvements in building design and construction. By understanding how the HERS Index works and its implications for energy savings, stakeholders can make informed decisions that enhance both economic and environmental outcomes.
The Increasing Importance of Energy Efficiency
In today’s construction landscape, energy efficiency has become a paramount concern for both residential and commercial projects. As energy costs continue to rise and environmental awareness grows, the demand for buildings that minimize energy consumption is increasing. Energy-efficient buildings not only reduce utility bills but also contribute to sustainability efforts by lowering greenhouse gas emissions. As a result, energy efficiency is now a key consideration in the design, engineering, construction, and renovation of buildings, making tools and metrics that measure energy performance, like the HERS Index, more critical than ever.
What is the HERS Index in the Home Energy Rating System?
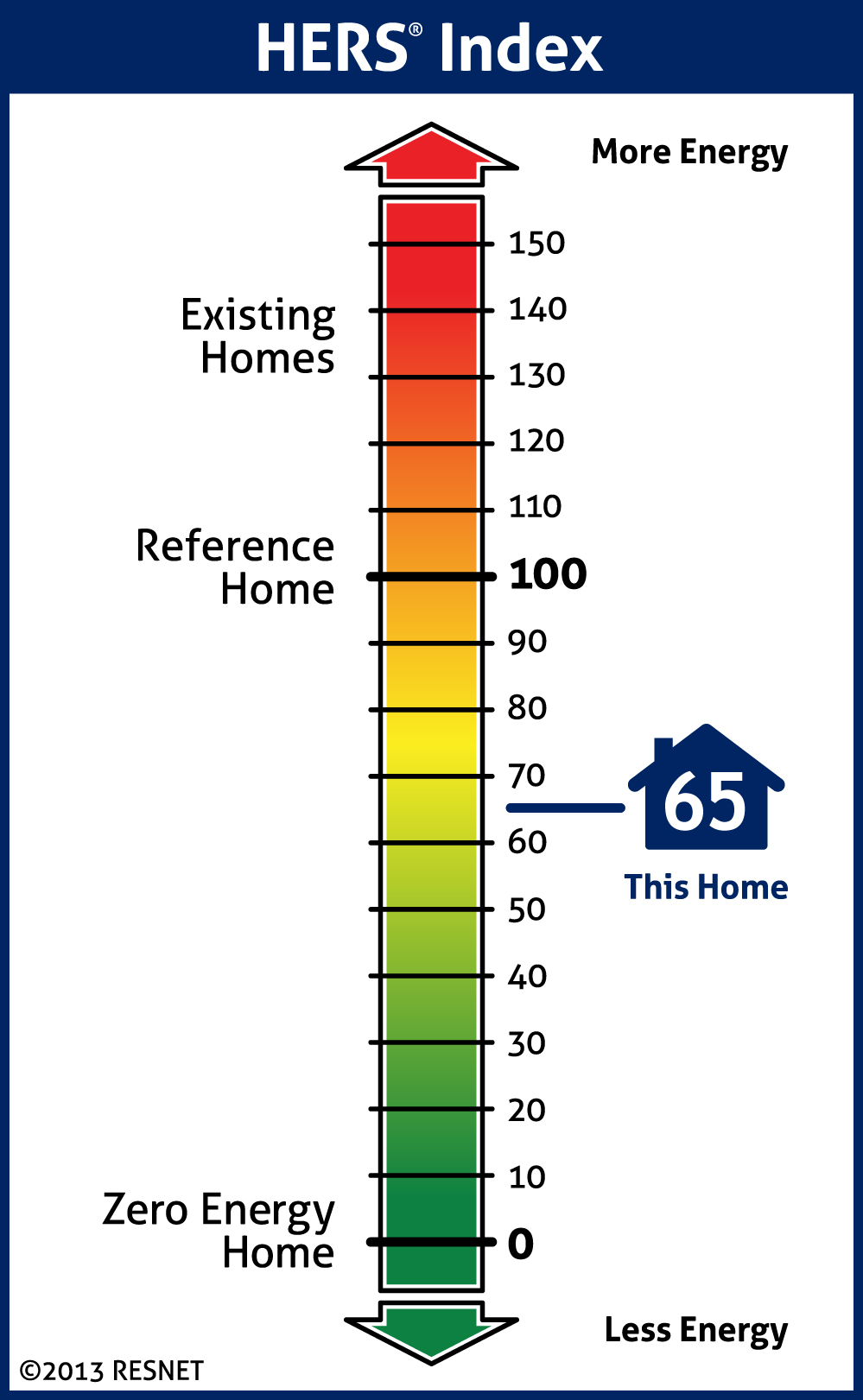
The Home Energy Rating System (HERS) Index is a nationally recognized scoring system for measuring a home’s energy performance. Developed by the Residential Energy Services Network (RESNET), the HERS Index provides a standardized method for evaluating and comparing the energy efficiency of homes. The index ranges from 0 to 150, with a lower score indicating greater energy efficiency. The HERS Index is determined through a comprehensive assessment performed by home energy raters, who conduct inspections, tests, and energy modeling.
The Importance of HERS Analysis and Reporting in Commercial & Residential Construction
The HERS analysis and reporting process plays a vital role in both commercial and residential construction by providing an objective measure of a building’s energy performance. For residential projects, a low HERS score can enhance the marketability of homes, as buyers are increasingly seeking properties with lower operating costs and reduced environmental impact. In commercial construction, HERS ratings are essential for meeting energy codes and standards, obtaining certifications like LEED, and qualifying for energy efficiency incentives and rebates.
Furthermore, the detailed reports generated from HERS analyses offer actionable insights for builders and developers. These reports highlight specific areas where energy efficiency can be improved, such as insulation, windows, HVAC systems, and ductwork. By addressing these recommendations, project stakeholders can enhance the overall energy performance of their projects, leading to reduced energy bills and improved comfort for occupants.
In summary, the HERS Index provides a clear and measurable way to achieve and demonstrate energy efficiency. Its application not only helps in meeting regulatory requirements but also adds value to buildings, ensuring they meet the growing demand for sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
How is the HERS Index Calculated?
Calculating a home’s energy performance using the HERS Index involves a multi-step process carried out by certified RESNET HERS raters, who use specialized tools and software to evaluate various aspects of the home’s energy use. Certified RESNET HERS raters undergo rigorous training to evaluate the home’s energy performance accurately. Their assessments provide valuable insights into the home’s energy usage and potential areas for improvement.
Calculation Process
Here’s an in-depth look at how the HERS Index is calculated:
- Energy modeling: Using specialized software, the rater inputs the collected data based on design documents to create a detailed energy model of the home. This model simulates the home’s energy performance under various conditions.
- Comparison to reference home: The energy model is compared to a RESNET reference home built to the 2006 IECC standards. The software calculates the difference in energy consumption, which is used to determine the HERS Index score.
- Final report: The rater provides a comprehensive report detailing the HERS Index score and identifying specific areas where energy efficiency improvements can be made.
- Inspections & Testing: The HERS rater performs on-site inspections, verifying the home’s design, materials, and energy systems. This includes a blower door test to measure air leakage and duct blaster tests for ductwork.
By meticulously analyzing these variables and following a standardized methodology, the HERS Index provides a reliable and actionable measure of a home’s energy efficiency, enabling homeowners and industry professionals to make informed decisions about energy upgrades and improvements.
Range of Possible Scores and Their Meanings
The HERS Index score ranges from 0 to 150, where a lower score indicates higher energy efficiency.
- Score of 0: Represents a home that produces as much energy as it consumes annually, typically achieved through a combination of high-efficiency design and renewable energy systems. Also referred to as a net-zero energy home.
- Score of 100: Indicates a home that meets the energy efficiency standards of the 2006 IECC. This serves as the baseline for the HERS Index.
- Scores above 100: Denote homes that consume more energy than the reference home, indicating less energy efficiency.
- Scores below 100: Reflect homes that are more energy-efficient than the standard new home, with each point decrease representing a 1% improvement in energy efficiency.
Variables Included in a HERS Rating
The calculation of the HERS Index involves analyzing several key variables that influence a home’s energy performance and energy consumption. These include:
Building Envelope
- Insulation levels: Assessing the quality and quantity of insulation in walls, floors, ceilings, and attics to ensure it meets or exceeds current standards.
- Air sealing: Evaluating the tightness of the building envelope to minimize air leaks, which can significantly impact heating and cooling loads.
- Windows and doors: Inspecting the thermal performance of windows and doors, including their U-factor and Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC).

HVAC Systems
- Heating efficiency: Measuring the efficiency of heating equipment, such as furnaces and heat pumps, often expressed in terms of Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) or Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF).
- Cooling efficiency: Evaluating air conditioning units and heat pumps based on their SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) or EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio).
Ductwork
- Leakage testing: Conducting duct leakage tests to identify and quantify air leaks in the duct system, which can lead to significant energy loss.
- Insulation: Ensuring ducts are properly insulated to reduce energy loss during air distribution.
Water Heating Systems
- Efficiency rating: Assessing the energy efficiency of water heaters, including tankless, solar, and heat pump water heaters.
- Distribution system: Evaluating the design and insulation of hot water distribution systems to minimize energy losses.
Lighting and Appliances
- Energy-efficient lighting: Considering the use of LED or CFL lighting, which consume significantly less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs.
- ENERGY STAR Appliances: Including refrigerators, dishwashers, and other major appliances that meet ENERGY STAR criteria for energy efficiency.
On-site Renewable Energy Systems:
- Solar panels: Calculating the contribution of photovoltaic systems to the home’s overall energy production.
- Wind turbines: Assessing the energy generation from wind turbines, where applicable.
This guide outlines key factors such as windows, insulation, mechanical efficiency, LED lighting, and square footage, detailing how each can boost or negatively impact the score.
Significance of HERS Rating in Sustainable Design
The HERS Index is a cornerstone of sustainable home design, offering a quantifiable measure of a home’s energy efficiency. By providing detailed insights into energy usage, the HERS Index helps drive improvements in energy performance, contributing to more sustainable and cost-effective living environments.
“Energy-rated homes are held to an extra high standard,” notes Morgan Poulos Keating, PE, a senior project engineer with DiLandro Andrews Engineering. “An excellent energy rating is synonymous with high quality in the building world. Homeowners can expect to be comfortable and pay less for energy now and in the future.”
How Energy Ratings Transform Home Efficiency
The HERS Index plays a pivotal role in promoting sustainable design by providing a standardized measure of a home’s energy performance. This energy rating system empowers homeowners, builders, and architects to make informed decisions that enhance energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact. By quantifying energy use and identifying areas for improvement, the HERS Index drives the adoption of energy-efficient practices and technologies, leading to:
- Reduced energy consumption: Homes with lower HERS scores consume less energy, resulting in significant cost savings on energy bills and a lower carbon footprint.
- Improved comfort: Energy-efficient homes maintain more consistent indoor temperatures and better air quality, enhancing overall comfort for occupants.
- Increased home value: High energy efficiency ratings are increasingly recognized as valuable assets, often leading to higher resale values and marketability.
- Compliance with regulations: Many building codes and green building standards now incorporate HERS Index requirements, ensuring that new construction meet stringent energy efficiency criteria.
DAE’s Expertise and Experience
At DAE, we have extensive expertise and experience in leveraging the HERS Index to optimize home energy performance. Our team of certified RESNET HERS raters employs state-of-the-art tools and methodologies to deliver accurate energy ratings and actionable engineering solutions on projects.
Our team is also certified to perform all code-required inspections and performance testing, including blower door tests.
HERS Rating Calculator
One of the key tools in our arsenal is the HERS rating calculator. This advanced tool assists in determining whether a HERS rating is necessary for residential construction projects in Suffolk County, NY. By answering a few targeted questions, users can gauge if their project might trigger the requirement for a HERS Rating.
- Guidance tool: The HERS rating calculator offers a preliminary assessment, helping users understand if a HERS rating might be required based on local municipal rules and the specifics of the proposed work.
- Professional judgment: While the calculator provides valuable insights, it is not a substitute for professional judgment. Engaging a design professional early in the project is crucial to avoid confusion and delays.
- Consultation available: Our team of experts is ready to help! We are happy to have detailed discussions to review all available facts and documentation, ensuring you receive accurate and tailored guidance.
Our commitment to excellence in energy ratings not only helps homeowners achieve superior energy efficiency but also supports broader sustainability goals. By integrating the HERS Index into our design and evaluation processes, we contribute to the creation of environmentally responsible and resilient homes.
How Energy Ratings Transform Home Efficiency
Energy ratings, such as the HERS Index, have a transformative impact on a home’s energy efficiency and overall living standards. This section delves into the specific benefits that energy ratings bring to homeowners and the broader community.
Impact on Energy Efficiency and Lower Energy Costs
Energy ratings pinpoint inefficiencies in a home’s design and systems, providing a roadmap for targeted upgrades. By addressing these areas, homeowners can achieve substantial reductions in energy consumption, leading to lower utility bills. Energy-efficient homes often feature advanced insulation, high-efficiency heating and cooling systems, and energy-saving appliances, all contributing to reduced operational costs and less strain on the energy grid.
Heightened Comfort and Better Quality of Life
The improvements driven by energy ratings go beyond cost savings. Enhanced insulation and air sealing create a more consistent indoor climate, reducing temperature fluctuations and eliminating drafts. High-efficiency HVAC systems ensure superior air quality and quieter operation. Together, these upgrades result in a more comfortable and healthier living environment, directly enhancing the occupants’ quality of life.
Higher-Value and More Environmentally Sustainable Homes
Homes with high energy efficiency ratings are increasingly in demand. Buyers recognize the long-term benefits of lower energy costs and the positive environmental impact, often resulting in higher resale values for these properties. Energy-efficient homes contribute to environmental sustainability by minimizing greenhouse gas emissions and reducing dependency on fossil fuels. Incorporating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, further bolsters a home’s eco-friendly credentials, appealing to environmentally conscious buyers.
The Path Forward in Energy Efficiency
As the pursuit of energy efficiency becomes increasingly vital in both residential and commercial construction, the HERS Index stands out as a pivotal tool for architects, builders, and homeowners. By offering a detailed and standardized measure of a home’s energy performance, the HERS Index not only aids in identifying areas for improvement but also drives the adoption of energy-efficient practices. Embracing these standards and methodologies is key to the future of energy-efficient construction and ensuring a greener, more sustainable world for generations to come.